Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis Topic Guide
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
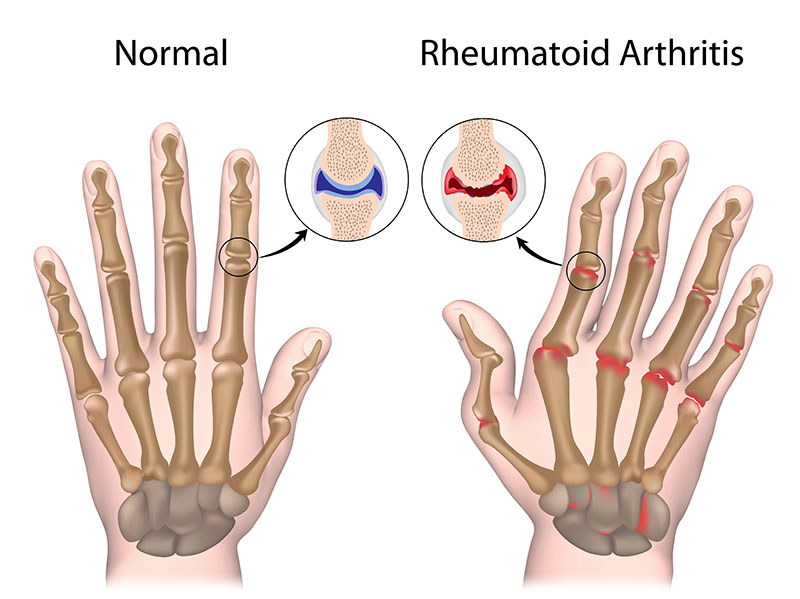
Rheumatoid arthritis, or RA, is an autoimmune disease that causes your immune system to attack healthy cells in your body. This attack causes inflammation in the parts of your body that are affected.
RA attacks many joints simultaneously and is most common in the hands, wrists, and knees. When a joint is affected by RA, the joints lining becomes inflamed, leading to long-lasting chronic pain, lack of balance, and deformities.
Addressing RA flares as early as possible helps prevent lasting joint damage. If you think you may be in an RA flare, contact your provider as soon as possible.

Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
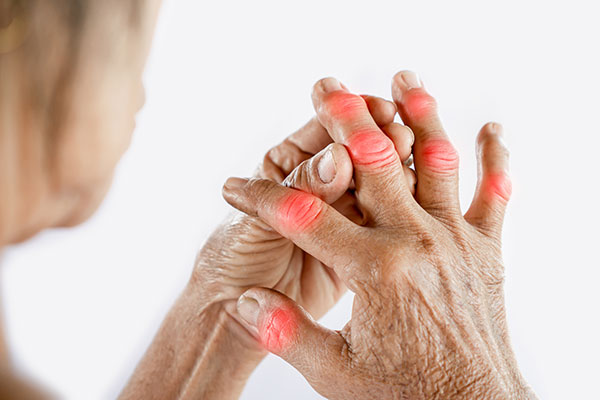
Signs and Symptoms of RA may include:
- Aching and pain in more than one joint
- Stiffness in more than one joint
- Swelling and/or tenderness in more than one joint
- Symptoms that are mirrored on both sides of the body (such as both hands)
- Weight loss
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Weakness
While the cause of RA is unknown, some risk factors may increase the likelihood of someone developing RA; these risk factors can be genetic or environmental and include:
- Age – RA is possible at any age, but likelihood increases with age
- Sex – cases of RA are higher in women
- Smoking
- History of live birth – women who have never given birth may be at a higher risk of developing RA
- Obesity

How is Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosed?
To diagnose RA, your provider will review your symptoms and history and conduct a physical examination where they will check for swelling, redness, and warmth. They may also check your reflexes and muscle strength. Additionally, X-rays and lab tests may be ordered.
Treatment for Rheumatoid Arthritis
- NSAIDs/Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory drugs – over-the-counter drugs such as ibuprofen and naproxen can help reduce mild pain and swelling in joints and muscles
- Corticosteroids – corticosteroids such as prednisone may help reduce swelling, pain, and tenderness. High doses can calm the system and help treat flares quickly, and then your provider will gradually lower the amount.
- Immunosuppressive medications such as methotrexate may be used if NSAIDs do not work
- Biologic medicines can significantly assist pain management, reducing inflammation and overall quality of life. Your AARA provider may recommend one of these treatments; infusion drugs can be administered in our in-office infusion suites.
- Biosimilars
Arizona Arthritis & Rheumatology Associates for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Options
The physicians in practice at Arizona Arthritis & Rheumatology Associates and their research division Arizona Arthritis & Rheumatology Research are dedicated to the care of patients with RA. They helped develop the available RA therapies and are investigating new drugs on the horizon. We encourage patients with RA to contact us to participate in our growing research efforts and to become patients of our cutting edge rheumatology center.



